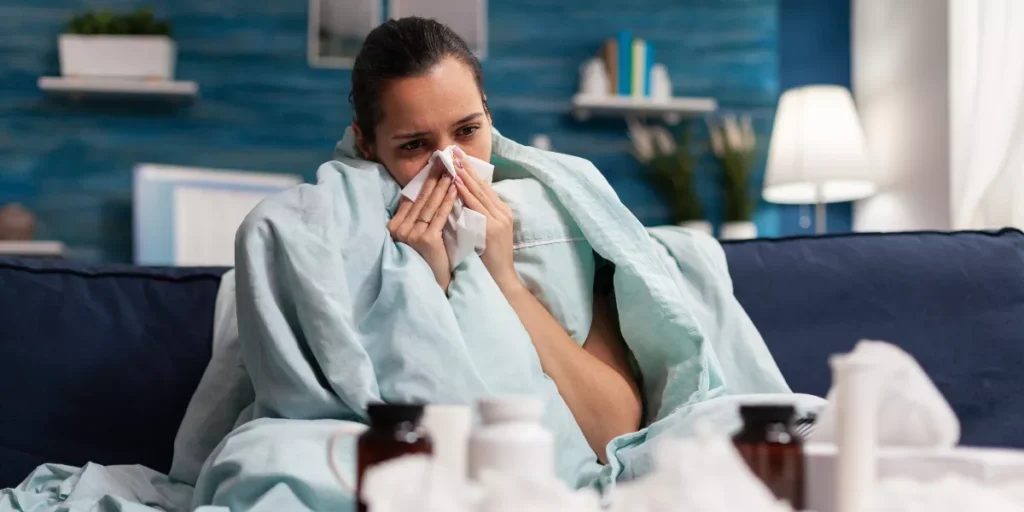
Have you ever wondered why women seem to experience stress differently than men? The answer lies in a complex interplay of biological, hormonal, and societal influences that shape how stress manifests in each gender. From the way women’s bodies chemically react to stressors to the expectations society places on how they should handle emotional challenges, the reasons behind these differences are multifaceted and intriguing. Understanding these nuances can provide valuable insights into the diverse ways in which stress impacts men and women.
Biological Differences
When considering stress symptoms, men and women exhibit varying biological responses that contribute to the differences observed. One key factor is how your body releases hormones in response to stress. For instance, men tend to have a ‘fight or flight’ response, where adrenaline and cortisol levels surge, preparing them for physical action. On the other hand, women often display a ‘tend and befriend’ response, releasing oxytocin that promotes bonding and seeking social support during stressful times.
In addition to hormonal variations, the brain plays a crucial role in how stress is processed differently between genders. The amygdala, responsible for processing emotions, tends to be more reactive in women, leading to heightened emotional responses. Meanwhile, the prefrontal cortex, involved in decision-making and impulse control, shows more activity in men when under stress, potentially affecting how they regulate their emotions and behavior.
Understanding these biological distinctions can help tailor stress management techniques to be more effective based on gender-specific responses. By recognizing and addressing these differences, individuals can better cope with stress and improve their overall well-being.
Hormonal Factors
Consider how hormonal factors play a significant role in influencing stress symptoms differently between men and women. Hormones like cortisol and oxytocin can affect how stress manifests in the body.
In women, fluctuating levels of estrogen and progesterone throughout the menstrual cycle can impact their stress responses. For example, during the premenstrual phase, when estrogen levels drop, women may experience increased stress sensitivity. Additionally, oxytocin, known as the ‘love hormone,’ is thought to help buffer stress responses and promote social bonding, which may lead to women seeking social support when stressed.
On the other hand, men tend to have a more stable hormonal environment, with testosterone playing a role in modulating their stress responses. Testosterone has been linked to increased risk-taking behavior in response to stress, which can sometimes mask the symptoms of stress. Understanding these hormonal differences can provide insight into why men and women may exhibit varying stress symptoms and coping mechanisms.
Societal Expectations
Hormonal factors play a significant role in influencing stress symptoms differently between men and women. Society’s expectations further contribute to these differences by shaping how individuals perceive and respond to stress.
Society often expects men to exhibit strength, resilience, and emotional restraint in the face of stress. This can lead men to downplay or internalize their stress, potentially manifesting in physical symptoms such as headaches or digestive issues.
On the other hand, women are often expected to be nurturing, sensitive, and emotionally expressive. These societal norms may result in women experiencing stress more acutely, leading to symptoms like anxiety, insomnia, or mood swings.
Additionally, societal pressure on women to balance multiple roles, such as career, family, and caregiving, can exacerbate stress levels. By understanding and challenging these societal expectations, individuals can develop healthier ways of coping with stress that aren’t limited by gender stereotypes.
Coping Mechanisms
To effectively manage stress symptoms, individuals can adopt various coping mechanisms that help alleviate emotional and physical strain. Engaging in regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or yoga, can significantly reduce stress levels by releasing endorphins and improving overall well-being.
Additionally, practicing mindfulness and meditation techniques can help calm the mind, reduce anxiety, and enhance resilience in the face of stressors. Connecting with supportive friends and family members through open communication or seeking professional help from a therapist can provide valuable emotional support during challenging times.
Setting boundaries, learning to say no, and prioritizing self-care are essential strategies in managing stress effectively. Furthermore, engaging in hobbies, creative outlets, or relaxation techniques like deep breathing exercises or listening to music can offer moments of relaxation and rejuvenation.
Health and fitness